Connecting to MySQL Server
In this section, we are going to cover how to use MySQL Server in Labs. If you would like to learn Database Management with MySQL Server, this is how you do.
Practice SQL queries, database design, and administration tasks with a production-grade MySQL server in your lab environment.
Getting Started
Step 1: Access Services
From the left window pane, click on Services.
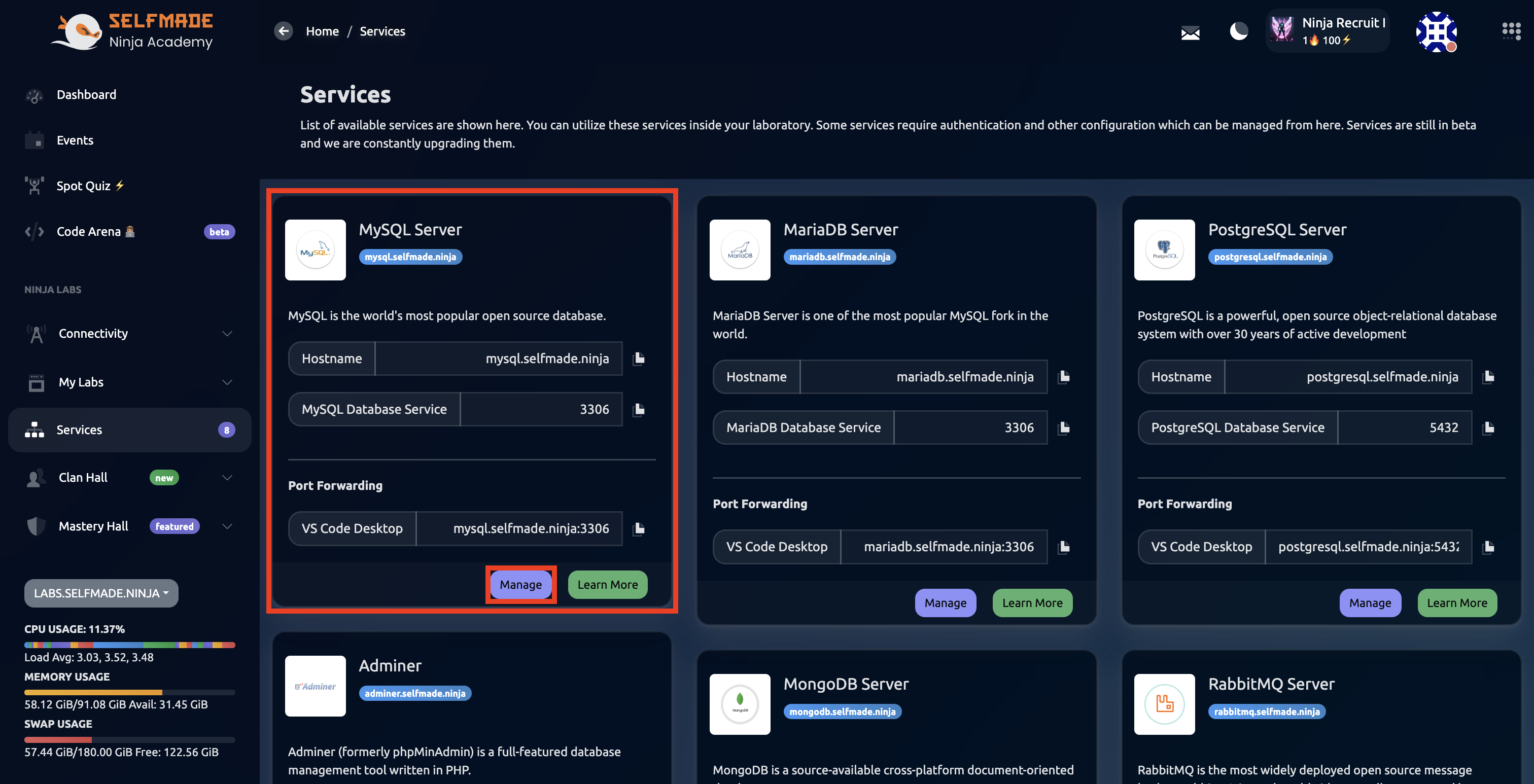
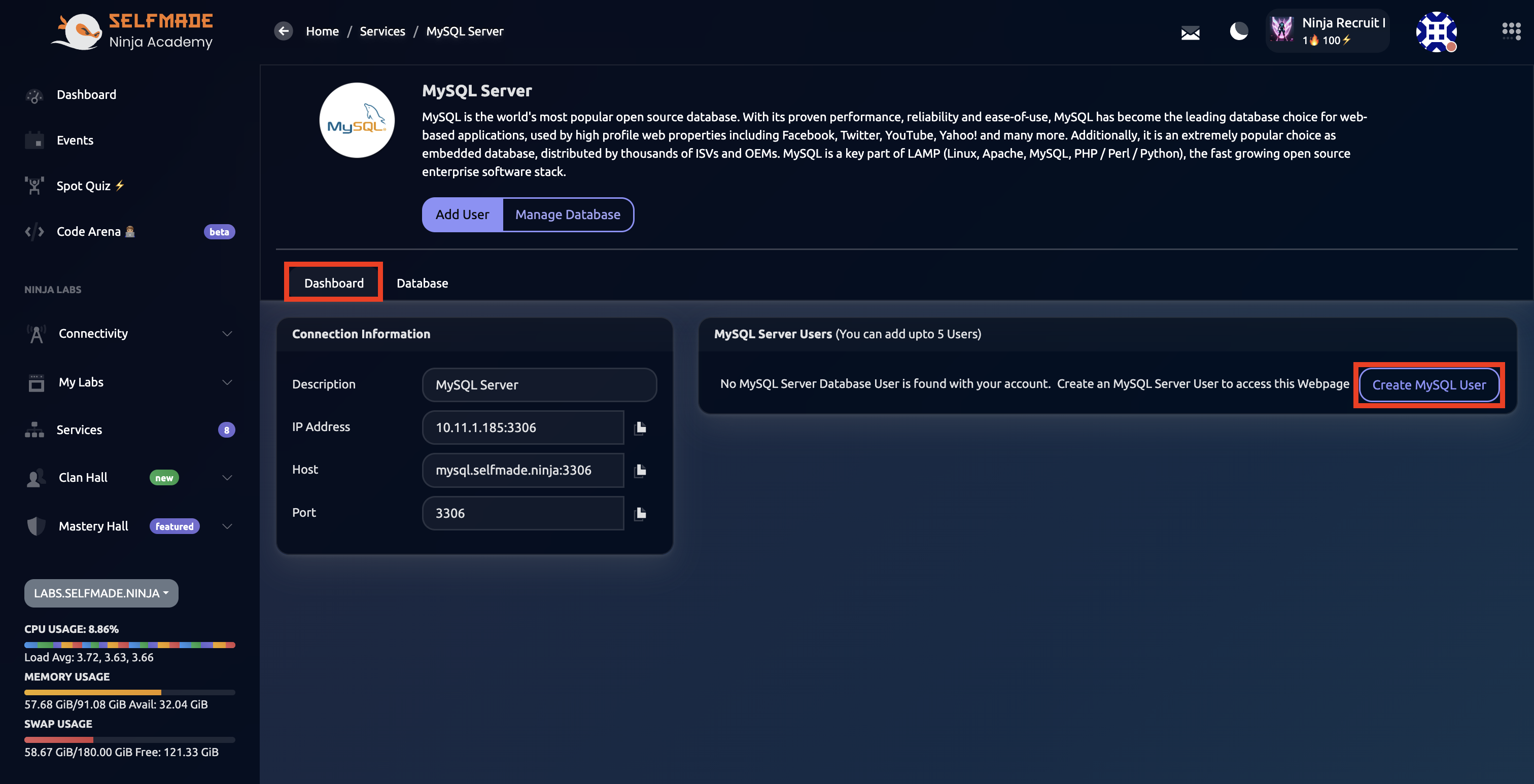
Step 2: Create MySQL User
Then, under Dashboard, click on "Create MySQL User"
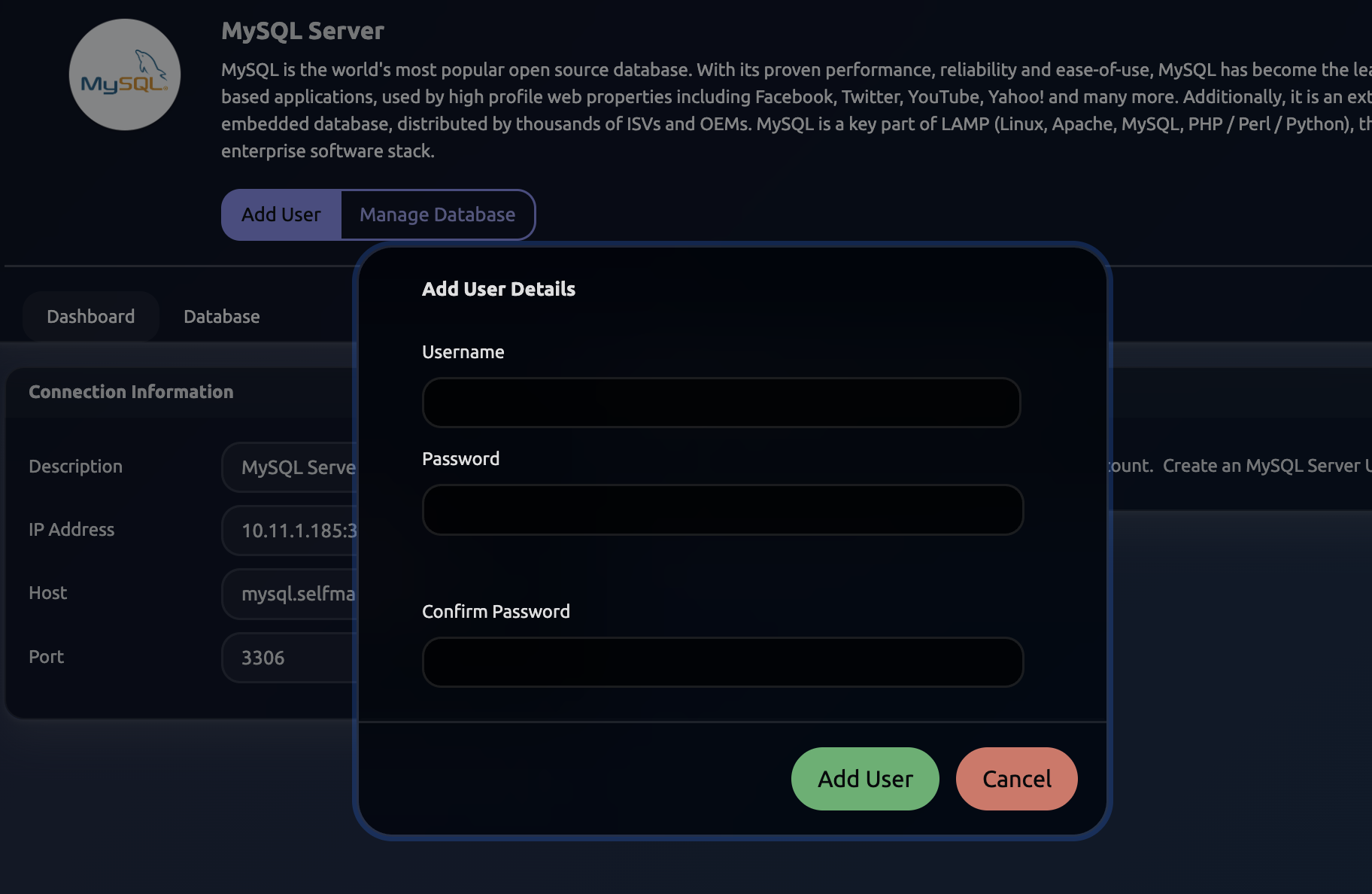
Enter the necessary details and click on Add User.
The Database name will follow the syntax: username_databasename
Database Setup
Create MySQL Database
Now, after creating a user, we need to create a MySQL Database in order for us to work in this server. To do that, click on the Database button and fill in the necessary information and then click on Create Database.
Lab Environment Setup
Deploy Essential Labs
After creating the Database, head to Machine Labs and then Deploy Essential Labs. Then click on Code and then click on Launch Code IDE.
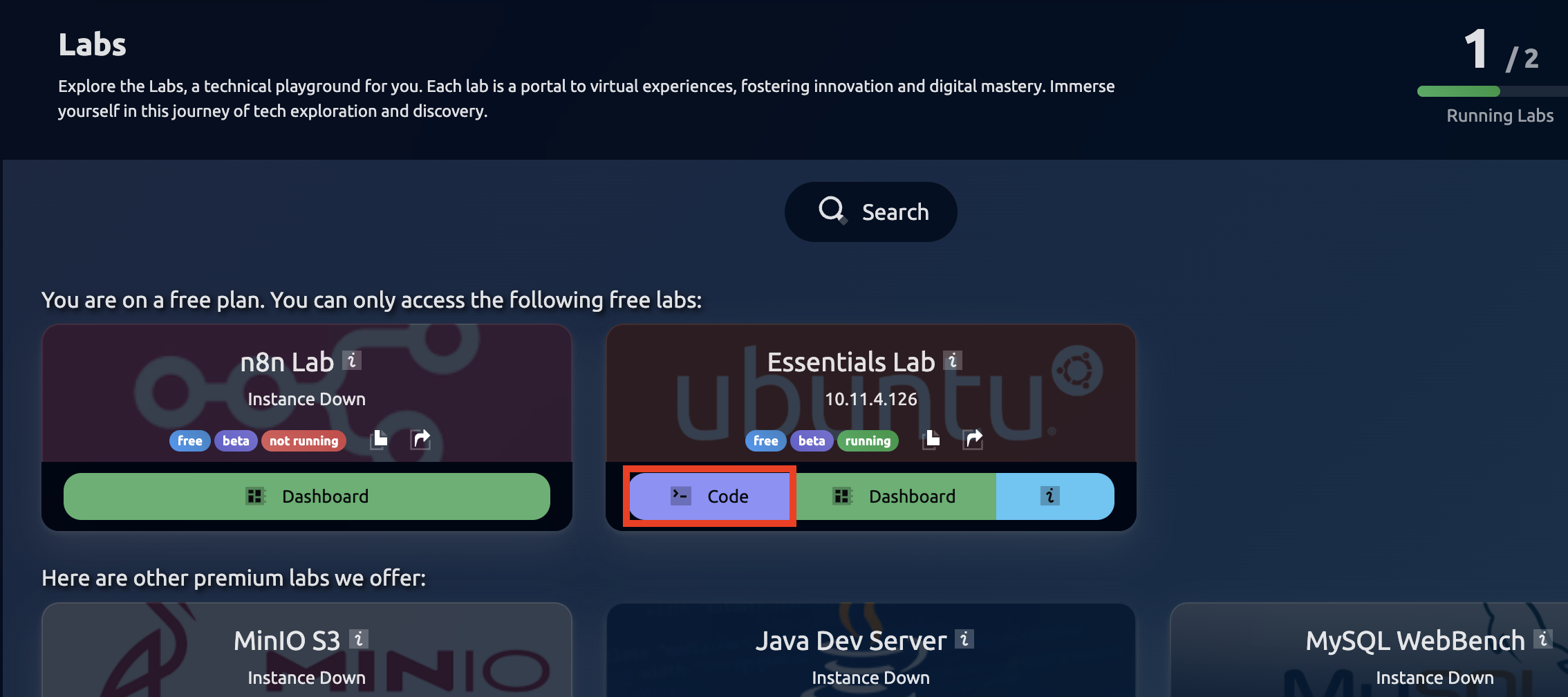
Then click on Code and then click on Launch Code IDE. This will open VS Code in your local browser.
VS Code provides a complete development environment with MySQL connectivity tools and database management capabilities.
Connecting to MySQL
Step 1: Get Connection Command
Now, go back to services dashboard and then find Adminer service and then copy the VS Code Web ($) value, which will look something like "socat TCP-LISTEN..%%.
Step 2: Execute Connection
Once you copy this code, head to VS Code that you launched and then open a new Terminal and paste the copied code.
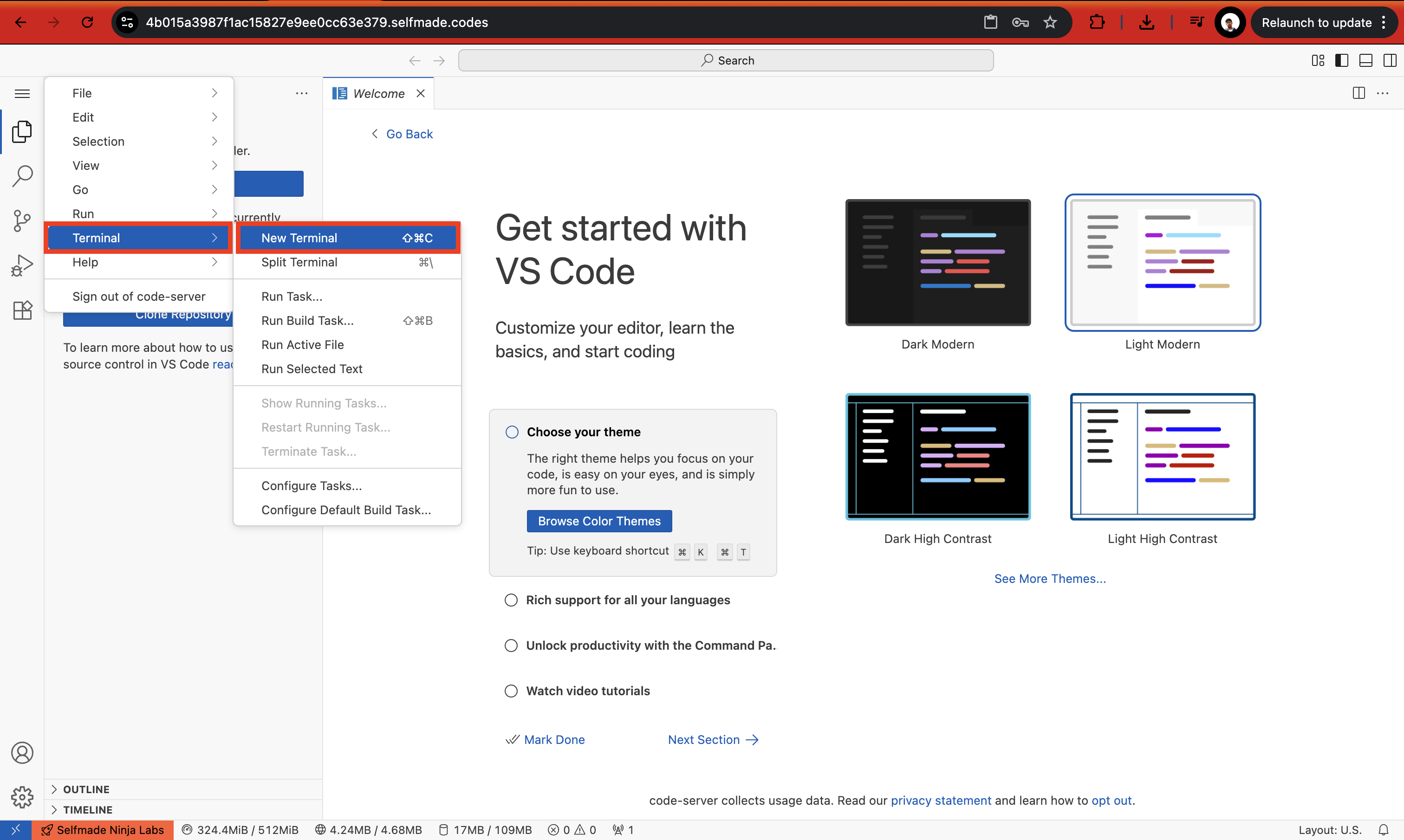
This will launch the MySQL Server in another tab. Enter the username, password and the database name and then click on Login.
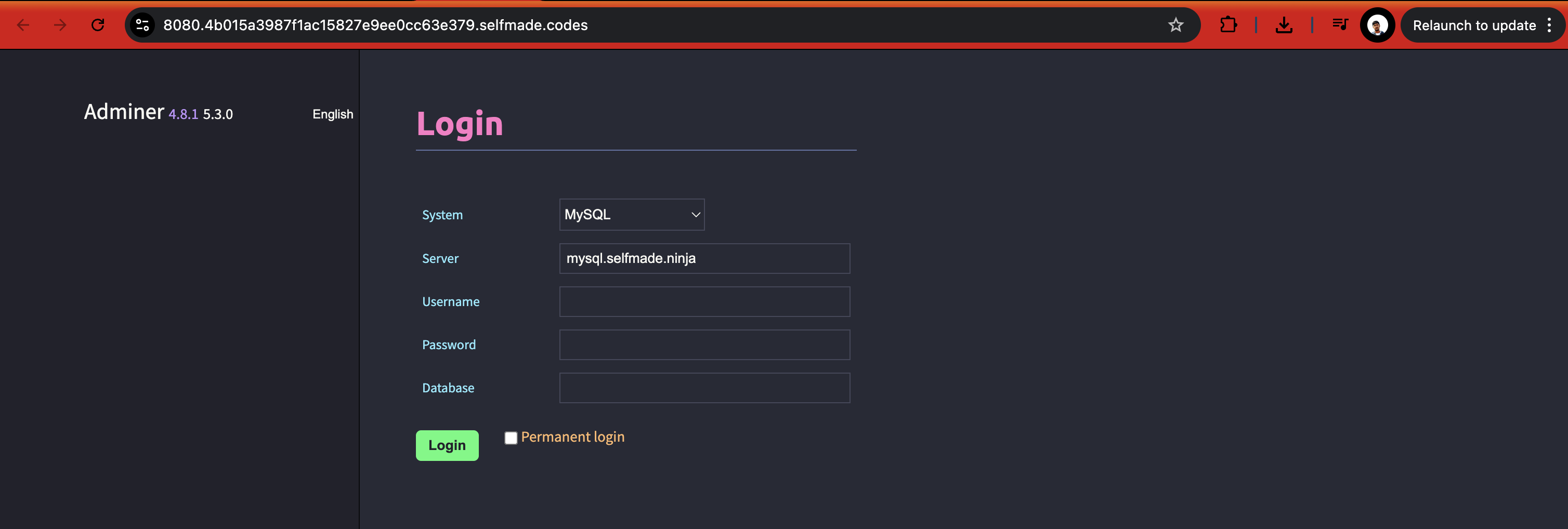
Once you login, you'll have full access to your MySQL database through the Adminer interface.
Working with MySQL
Once you login, it will look something like this:
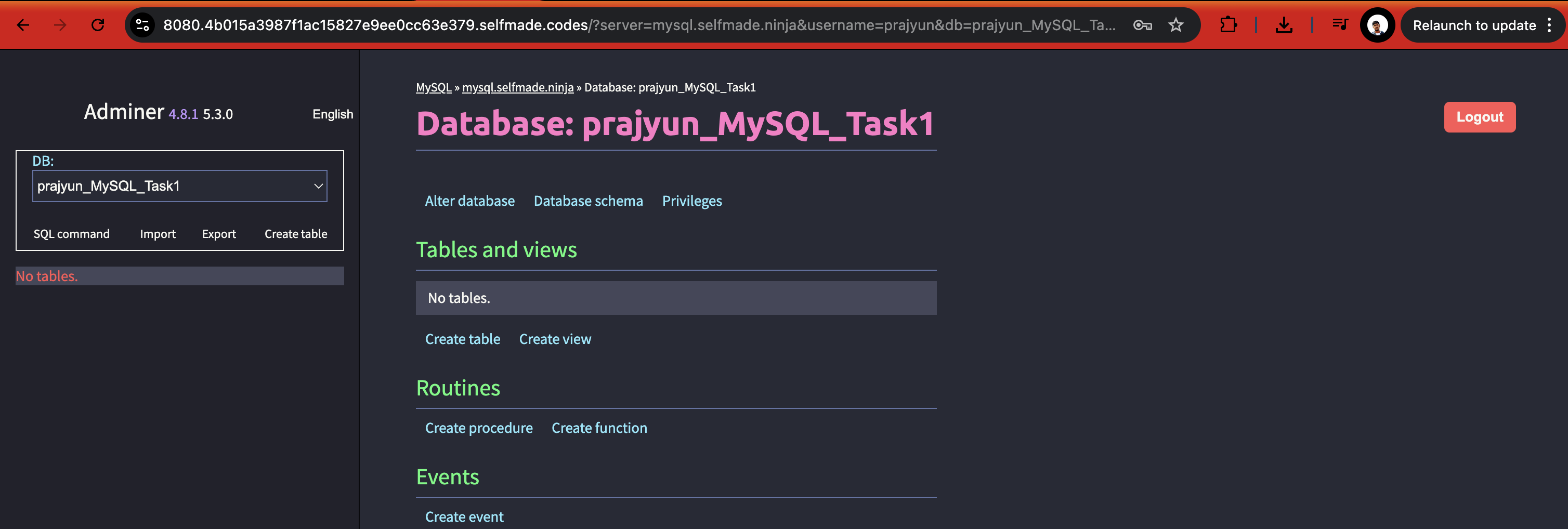
What You Can Do
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Tables | Design and create database tables |
| Execute Queries | Run SQL commands and queries |
| Manage Data | Insert, update, and delete records |
| Database Administration | Manage users, permissions, and settings |
- Always backup your data before making structural changes
- Use proper indexing for query performance
- Follow SQL naming conventions for tables and columns
- Test queries on sample data before running on production datasets